Important Economic Indicators by Country
In this section we will give you a quick overview of the economy of each of the Major currency pairs and the most important fundamentals releases for each one of them.
Note however, that this list is provided “as is” and may not reflect what happens in the real world. Use this only for informational purposes and on your own risk.
European Economy and Monetary Union (EMU) – EUR
EMU Quick Economic Facts
The EMU (European Economic and Monetary Union) consists of 16 member countries: Austria, Belgium, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Ireland, Italy, Luxemburg, Netherlands, Portugal, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Norway and The United Kingdom. However, Sweden, Norway and The United Kingdom have not entered the last stage of the EMU where they adopt the Euro as their currency; they still use their own currency.
Eurozone is a common term used for those countries that have adopted the Euro as their Currency.
Eurozone Countries and their GDP
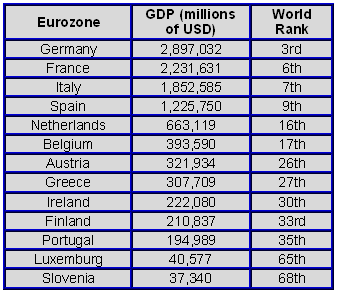
[Table 1]
Source: International Monetary Fund (2006)
According to the International Monetary Fund, if the European Union (EU) was a country, it would be the only one in the world with a largest GDP than the US with 14.5 trillion USD.
Aside from a common currency, Eurozone countries share a single monetary policy dictated by the European Central Bank (ECB). The ECB has established strict rules for every member country which main focus are:
Stability of Prices
Low Inflation per country (below 1.5% of the average of the best three performing countries)
Low deficit
Growth
The importance of the EUR has grown considerably as more and more countries in the world switch their reserves from USD to EUR.
Important Economic Indicators for the EMU
European Interest Rate Announcement
Interest rates are a measurement of “the cost of money. The European Central Bank uses Interest rates as a tool to accomplish their most important goals: inflation, growth and stability of prices.
When the ECB lower (tightens up) their interest rates, the Euro tends to depreciate against other currencies as it yields lower returns (i.e. investors sell their Euros to buy other currencies with higher returns, increasing the offer of Euros thus prices go down).
When the ECB hikes their interest rates, the Euro tends to appreciate against other currencies as it yields higher returns (i.e. investors sell their local currency to buy increasing its demand thus prices go up).
News Source: http://www.ecb.int/press/pressconf/2006/html/index.en.html
NOTE: As we already know the EU consists of various countries and each one of them has its own figure, although its important to have an idea of the overall performance, for the following economic indicators it’s more important to monitor the performance of the top three or four countries of the EU (refer to the GDP per country in the Eurozone above).
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) from Germany and the Eurozone
The GDP of the EU is the value of services and Products produced within the borders of the EU. A good GDP reflects a healthy economy.
A good GDP figure indicates the economy is growing and the Euro tends to appreciate against other currencies.
In a bad GDP figure, the Euro tends to lose value against other currencies.
News Source: http://ec.europa.eu/comm/eurostat
Brain Feeder 1
What is a good or/and a bad or good figure or number? In the GDP we saw (as we will see in future economic indicators) a good GDP tends to appreciate the value of the Euro, what does “good” mean? A value above zero? Or perhaps a number larger than 50? Think on it and try to come to an answer. Once you think you have got it please go to the Summary Report where you will find the answer to this feeder.
Harmonised Consumer Price Index (HCPI) from Europe
HCPI is what the EU uses as a measurement for inflation and stability of prices. As we already explained above, the ECB has some rules for its members and one of the most important is that each country’s inflation should not deviate more than 1.5% of the average of the best three performing members.
Usually for the EU:
When a low HIPC number is released the Euro tends to gain value against other currencies.
When a high HIPC number is released the Euro tends to lose value against other currencies.
News Source: http://www.ecb.int/stats/prices/hicp/html/index.en.html
Brain Feeder 2
How is the European HCPI different from what other countries use as a measurement of inflation (like the US uses CPI)?
Unemployment Data from Germany and Europe
Employment is always a good indicator of the shape of the economy of all countries. Usually when unemployment numbers are low it reflects an economy in good shape (and vice versa).
Usually for the EU:
A low unemployment number tends to appreciate the value of the Euro against other currencies
A high unemployment data tends to depreciate the value of the Euro against other currencies.
News Source: http://ec.europa.eu/comm/eurostat
Trade Balance from Europe
The Trade Balance in the Eurozone measures the amount of services and products purchased (imports) against those sold to other countries (exports). Trade Balance of each country of the Eurozone is divided in two: Intra-Eurozone and Extra-Eurozone. Intra-Eurozone is the balance of each country of the Eurozone against the Eurozone and Extra-Eurozone is the balance between each country of the Eurozone against non-Eurozone countries.
Usually Intra-Eurozone data does not affect the currency market while Extra-Eurozone tends to affect the currency market.
A good trade balance number usually appreciates the value of the Euro against other currencies.
A bad trade balance number usually depreciates the value of the Euro against other currencies.
Most investors focus on the Trade Balance of Germany as it is the leading economy of the Eurozone.
News Source: http://ec.europa.eu/comm/eurostat
Industrial Production (German and European)
Industrial production of the Eurozone measures the total output of the manufacturing and energy sector. Sometimes the Industrial Production is used as a proxy variable to measure the GDP of any country.
Usually:
With a good number the Euro will gain value against other currencies
With a bad number the Euro will lose value against other currencies.
Most investors focus on Industrial Production of Germany as it is the leading economy of the Eurozone.
News Source: http://ec.europa.eu/comm/eurostat
ANOTHER NOTE: For the following economic indicators its ok to focus on the performance of Germany as it is the leading economy of the Eurozone.
IFO Business Climate Survey (Germany)
The IFO Survey is one of the most important sentiment indicators for the Euro Zone. This survey is conducted on over 7,000 enterprises of Germany and it is divided into two main areas: their current assessment of business climate and their expectations for the future business conditions. It is an index where 100 is the centerline between good and bad conditions.
Usually:
A good number (above 100) tends to appreciate the Euro against other currencies.
A bad number (below 100) tends to depreciate the Euro against other currencies.
This survey is conducted monthly.
News Source: http://www.cesifo-group.de/pls/portal/url/page/IFOHOME/A-WINFO/D1INDEX/10INDEXGSK
ZEW Survey (Germany)
This is survey is conducted by experts throughout Europe on their assessment about Germany’s economic expectation: inflation, growth, stock market and exchange rate over a medium term period (6 months) and their assessment of the current conditions.
With a good number, the Euro tends to gain value against other currencies.
With a bad number, the Euro tends to lose value against other currencies.
News Source: http://www.zew.de/en/publikationen/Konjunkturerwartungen/Konjunkturerwartungen.php3
What is the difference between the IFO and ZEW surveys?
The IFO survey is conducted by enterprises and business owners while the ZEW survey is conducted by experts in the area.
10-Year German Bund
Long term securities (governmental) are always a good indicator for future performance of any country. In fact, if you do some research, you will see that very few under-development countries have in fact 10-Year securities (because very few investors would invest in any long term security due to its uncertainty).
In this case, the 10-year Bund is a good indicator for the future performance of the Euro. When compared to the US 10-Year Bond:
If the Bund rates are higher and the differential increases: bull Euro sentiment
If the Bund rates are higher and the differential decreases: bear Euro sentiment
United States – USD
US Quick Economic Facts
Currently United States is the leading economic power in the world with a nominal GDP of 13.25 trillion USD, 3 times greater than Japan (which is the second in the world).
US has a very large trade deficit (the US is the largest trading partner for most countries in the world).
According to the Bank of International Settlements the USD is involved in 89% of all currency deals
The Federal Reserve (Central Bank of US) has two main economic goals: Price stability and Sustainable growth
The USD is perceived as one of the strongest and most stable currencies in the world and as a result many countries (mostly under-developed) peg their local currencies to the USD.
Important Economic Indicators for the USD
Non-farm Payrolls Report – “NFP” (US)
The NFP report is probably in the top three market movers in today’s markets.
The NFP shows the number of jobs created for a given month outside the agricultural industry and government agencies. It is a major indicator of the labor market strength, and the labor market is commonly tracked as an important domestic economy diagnosis.
A strong number indicates a healthy economy. Resultantly the USD could appreciate against other currencies
A weaker number indicates a lesser level of health in the economy. Resultantly the USD could depreciate against other currencies.
This report comes along with other data such as: the unemployment rate, which is the percentage of people actively looking for a job, but were not able to find one.
This report is commonly released on the first Friday of every month.
News Source: http://www.bls.gov/news.release/empsit.toc.htm
Interest Rate Decision (US FED)
Interest rates are a measure of “the cost of money”. Central banks use interest rates as a tool to accomplish certain goals and objectives- such as inflation, growth, etc.
An increase in US interest rates (hike) will typically increase the demand for the US Dollar, as foreign entities will sell their local currency and buy the USD to take advantage of the higher interest rate, pushing up the value of the USD.
Tightening interest rates (cut) will decrease the demand for USD, as foreign entities will buy back their local currency and sell USD, bringing back down its value.
Unchanged Interest rates could be bearish or bullish for the USD depending on the circumstances, unchanged interest rates after a period of tightening is perceived as USD bearishness and after a hiking cycle it could be perceived as USD bullishness.
This report is released 8 times a year.
News Source: http://federalreserve.gov/fomc/fundsrate.htm
Trade Balance from US
This measures the net exports and imports of goods and services of the US. This is the trade flows component of the balance of payments, which measures the demand and supply of one currency as explained before.
US has a negative trade balance against almost all countries in the world.
With a good number the USD is more likely to appreciate.
With a bad number the USD is more likely to depreciate
This report is released every two months (middle of the month following the reporting period.)
News Source: http://www.bea.gov/bea/di/home/trade.htm
US Consumer Price Index
It is an index designed to measure the change in price of a fixed basket of basic goods and services (inflation). It is intended to measure pure price changes while leaving out the changes in quality of goods and services.
If the CPI increases, the purchasing power of the currency decreases.
If the CPI decreases, the purchasing power of the currency increases.
This report is commonly released the second week of each month.
Core CPI excludes food and energy which are two of the most volatile components in the CPI measurement. This indicator shows a more stable version of price changes.
News Source: http://www.bls.gov/cpi/
Brain Feeder 3
Is there a good Inflation number for all countries?
Consumer Confidence Index from US
The CCI is a survey conducted over 5000 consumers. They are asked questions about how they perceive the economy, current business conditions, what they expect for the future, etc. It measures how confident the consumers are in a given month.
A good CCI number indicates that the economy is in good shape, and the USD appreciates.
A bad number indicates something is wrong with the domestic economy, therefore USD depreciates.
In a CCI release day, the average range for the EUR/USD is 129 pips.
Release date: close to the end of each month.
News Source: http://www.bls.gov/cpi/
US Retail Sales
Retail Sales is an indicator of consumer expenditure. It measures the sales of retail stores (including durable and non-durable goods), and excludes services (major weakness of this indicator).
A high number indicates favorable economic conditions, and the currency tends to increase its value.
A low number indicates non favorable economic conditions, and the currency tends to decrease its value.
Release date: near the middle of each month.
News Source: http://www.census.gov/svsd/www/advtable.html
Gross Domestic Product from US
Measures the value of goods and services (total production) produced within the borders of the United States. GDP includes: consumption, private investments, government expenditure and exports less imports.
The most important component of this announcement is the change (in GDP) between the actual month and the same month of the previous year.
A good number indicates a strong economy, currency tends to increase its value.
A bad number indicates a weak economy, currency tends to decrease its value.
News Source: http://www.bea.gov/bea/dn/home/gdp.htm
ISM Manufacturing Index from US
ISM stands for “Institute of Management Suppliers”. It is a survey conducted over business executives on their assessment for future business conditions. This indicator it’s important because the ISM is usually the first indicator that turns around after a period of recession or constant growth.
The ISM values range around 50, where values above 50 mean an “expansion” or good expectation; and values below 20 mean “contraction” or bad expectations for the near future.
News Source: http://www.ism.ws/ISMReport/index.cfm
Minutes of FOMC (FED)
Minutes of the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) give some insight about the monetary policy decision (three weeks after their actual monetary policy decision).
Usually investors and traders focus on key elements of how the Federal Reserve see current economic conditions, what they expect for the future and general commentaries on market indicators such as inflation.
The market reaction to the FOMC Minutes varies as the information is already priced, but when they give evidence of a “Hawkish” outlook interest rates hikes are more likely, on the other hand if they give evidence of a “Dovish” outlook, interest rates cuts are most likely.
Japan – JPY
Japan Quick Economic Facts
Japan is the world’s second largest economy by nominal GDP with 4.4 trillion USD.
Japan is one of the Worlds largest exporters in the world. A good percentage of their GDP accounts for exports (close to 15%).
The Bank of Japan is the responsible for handling the monetary policy of Japan. The Bank of Japan is very active in the Forex markets. It is known that when the USDJPY approaches to 100.00 the B of J tends to intervene in the market pushing the prices up. It’s important to remember that Japan is a net exporter so it is in their best interests to have a cheaper currency than other majors; this way foreigners can buy more Japanese goods and services for less of their local currency.
From the Major Currencies, the JPY is the currency with the lowest interest rate. This makes JPY crosses (such as GBPJPY or EURJPY) interesting for carry traders (those who look to profit from interest rate differentials via rollover).
Although the Minister of Finance no longer officially dictates monetary policy, they still have some influence in exchange rates and monetary policy.
Important Economic Indicators for the JPY
Japanese Interest Rate Announcement
The Bank of Japan is responsible for the monetary policy of Japan. Currently, Japan is the country with the lowest interest rates (from the majors). The BoJ meets once per month to announce possible changes in their current monetary policy and economic outlook.
An increase in Japan’s interest rates might lead to JPY appreciation
A decrease in interest rates might lead to JPY depreciation.
News Source: http://www.boj.or.jp/en/theme/seisaku/kettei/index.htm
Gross Domestic Product – GDP from Japan
GDP is the sum of all goods and services produced within the borders of Japan. Consumption, private investments, government expenditure and exports less imports are the elements of GDP or growth.
With a good number the JPY might gain value
With a bad number the JPY might lose value
News Source: http://www.esri.cao.go.jp/en/sna/menu.html#93sna
Tankan Survey (Japan)
As other sentiment indexes, the Tankan survey is conducted on companies which are queried about their overall economic outlook (including business conditions).
This report is very important for both foreign investors and the Bank of Japan as it gives a picture of the current and the near future economic conditions. This helps investors allocate their capital or the BoJ to determine its policy.
A positive number means a good outlook while a negative number means a negative outlook.
A better than expected number usually helps the JPY gain value.
A worse than expected number usually makes the JPY lose value.
News Source: http://www.boj.or.jp/en/theme/research/stat/tk/index.htm#r
Trade Balance (and Merchandise Trade Balance) from Japan
The trade balance measures the difference between exports vs. Imports. Japan is widely known as a net exporter country so the bigger this number the better for its economy.
A positive number indicates a surplus while a negative number indicates a deficit.
A better than expected number tends to appreciate the JPY
A worse than expected number tends to depreciate the JPY.
News Source: http://www.customs.go.jp/toukei/shinbun/happyou_e.htm
Merchandise Trade Balance is a similar economic indicator but only takes into accounts tangible goods such as those of the car and electronic industries (two of the most important industries for Japan).
Japan’s Employment Situation
This report is an analysis of the current and future conditions for the labor market in Japan. As always, the labor conditions are a very good indicator for the overall economy health and activity.
Japan’s Employment Situation Report unusually incorporates other important data such as consumer consumption data, increase/decrease of wages, inflationary pressures, etc.
With a good number the JPY tends to gain value
With a bad number the JPY tends to lose value
News Source: http://www.stat.go.jp/english/data
National Consumer Price Index (NCPI) from Japan
The NCPI is the most important indicator for inflation in Japan.
Unusually, Japan suffers from deflation (indicative of slow domestic activity) so a low number might not be good for the JPY.
On the other hand, a high number might be good for the JPY as it indicates a more dynamic period for its domestic economy.
News Source: http://www.stat.go.jp/english/index.htm
BoJ Policy Minutes (BoJ)
This report usually comes a month later after the actual monetary policy decision. It clearly explains the reasons or why the BoJ hiked interest rates, cut interest rates, left them unchanged or other decisions.
Traders and investors try to focus on key elements that will give them evidence about how the policy makers see the economy in the near future to make their trading decision.
United Kingdom – GBP
UK Quick Economic Facts
The United Kingdom has the 5th largest economy in the world with a nominal GDP valued at over 2.3 trillion USD.
As with other leading economies in the world, the UK is a service oriented economy (mostly financial services: insurance and banking).
The UK has a very strong relationship with the Eurozone as imports and exports between both of them are around 50% of all UK’s trade balance.
The Bank of England (BoE) is responsible for the monetary policy in the UK. Bank of England’s main concern is to keep inflation at comfortable levels.
There has been an ongoing debate on whether or not the UK should join the Eurozone (countries adopting the Euro as their currency). Argument against: currently UK’s policies are doing well in the new global economy, they will no longer have control over their monetary policies and arguments in favor are: the power of the European Central Bank will increase dramatically.
The GBP is amongst the most liquid currencies in the world and due its high interest, traders and investors are interested in this currency to perform carry trades even when other currencies have higher interest rates.
Important Economic Indicators for the GBP
UK’s Interest Rate Announcement
The Bank of England meets monthly to announce their interest rate decision. Currently, the GBP is the best choice for carry traders (even when there are other majors with higher interest rates) because of its liquidity (the most important being the GBP/JPY and the GBP/USD). For this reason traders and investors watch closely Bank of England’s decision.
An increase in interest rates tends to appreciate the GBP value
A decrease in interest rates tends to depreciate the GBP value
Unchanged interest rates can be bullish or bearish depending on the circumstances.
News Source: http://www.bankofengland.co.uk/monetarypolicy/decisions.htm
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of the UK
The GDP shows the overall growth of the economy of United Kingdom.
With a good number the GBP tends to gain value.
With a bad number the GBP tends to lose value.
Sometimes excessive growth can lead to periods of high inflation which can lead to further interest rates hikes.
News Source: http://www.statistics.gov.uk/instantfigures.asp
UK’s Trade Balance
Trade balance measures the difference from exports and imports of the United Kingdom. The first trading partner for the UK is the Eurozone, but still on an individual basis, US remains the first one.
With a good number the GBP tends to gain value
With a bad number the GBP tends to gain value.
Another important trade balance announcement is the NON-EU Trade balance which measures the difference between exports and imports of non European countries.
Consumer Price Index (CPI) from the UK
Consumer Price Index is the key element of inflation. This is how most investors and traders measure inflation and thus the increase/decrease of their purchasing power.
For the UK commonly:
A low number tends to increase the value of the GBP
A high number tends to decrease the value of the GBP
Another measure of the CPI for the UK is the Core CPI which excludes food and energy, two of its most volatile components.
Minutes of BoE Meeting (BoE)
In the Minutes of the BoE Meeting policy makers share their views and the reasons why they made any change to the interest rate or indeed left it unchanged.
Most of the times traders and investors focus on the outlook for the future as the rate decision was already occurred. They try to find evidence as to whether or not a future increase/decrease is likely to happen in the next interest rate announcement.
For instance: if they mention “the housing market is in a clear expansion” it might create inflationary pressure which might lead policy makers to increase interest rates.
Canada – CAD
Canada Quick Economic Facts
Canada is currently the 8th largest economy in the world with a nominal GDP valued at 1.3 trillion USD.
Canada’s economy is highly dependant on its trade balance especially with the US who imports around three quarters of Canadian exports.
The Canadian Dollar has a very tight relationship (positive correlation) with commodities such as gold and oil.
The Bank of Canada is responsible for the monetary policy. BoC primary objective is price stability. Changes in policies can be made at any time as their councils meet almost every day.
Important Economic Indicators for the CAD
Interest Rate Decision of Canada
As in other countries rate decisions, it is of major importance to its exchange rate.
Typically an increase in interest rates might increase the demand for CAD increasing its value. Whilst an interest rate cut will reduce the demand for CAD decreasing its value.
Because of the interest rate announcement is a highly expected and anticipated announcement, traders and investors are more focused on the wording policy makers use to collect evidence about future economic conditions.
News Source: http://www.bankofcanada.ca/en/monetary/target.html
Canada’s International Merchandise Trade
This indicator measures the difference between exports and imports (excluding services). Canada’s major trade partner is the US which imports about 75% of Canada Exports.
Typically in a good number the CAD will gain value
And in a bad number the CAD will lose value against other majors.
News source: http://www.statcan.ca/english/Release/index.htm
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of Canada
The Canadian GDP measures the total production (and consumption) of goods and services produced within the Canadian borders.
A good number usually makes the CAD gain value
A bad number usually makes the CAD lose some value
GDP includes: Private consumption and investments, government expenditure and exports less imports.
News source: http://www.statcan.ca/english/Release/index.htm
Ivey Purchasing Managers Index (PMI)
175 corporate executives across Canada are queried about their purchases for the current month comparing them to the one previously.
With a good number the CAD might gain value
With a bad number the CAD might lose value against other majors.
A PMI value above 50 indicates expansion (better outlook) while a value below 50 indicates contraction (worse outlook).
News Source: http://iveypmi.uwo.ca/english/historic_data.htm
Consumer Price Index (CPI) of Canada
As with other countries, the CPI measures price stability among a basket of goods and services. It intends to measure inflation for a given period. An increase of inflation reduces the purchasing power of the CAD while a decrease of it increases its purchasing power.
A good number tends to appreciate the CAD
A bad number tends to appreciate the CAD
News Source: http://www.statcan.ca/english/Subjects/Cpi/cpi-en.htm
Change in Canada’s Employment
Employment data is always a good measurement of the health of the economy. This announcement is the net change in the number of people employed from one period to another.
A good number could make the CAD gain some value
A bad number could make the CAD lose some value.
News Source: http://www.statcan.ca/english/Subjects/Labour/LFS/lfs-en.htm
Australia – AUD
Australia Quick Economic Facts
Around 80% of Australia’s GDP come from services industries such as insurance, financial services and real state
The Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) is responsible for the monetary policy. RBA main objectives are to: control inflation, stability of the exchange rate and low unemployment. Each month its members meet to discuss possible changes to the monetary policy.
The AUD has a very strong relationship (positive correlated) to commodities, especially gold prices.
Currently amongst the Majors, Australia has the highest interest rate at 6.75% (as of late 2007) making this currency interesting for carry traders.
Important Economic Indicators for the AUD
Interest Rate Decision of Australia
The Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) is Australia’s Central Bank and is responsible for changes in monetary policy including interest rates.
From the major currencies Australia is the country with the highest interest rate valued at 6.75% (as of late 2007). The RBA normally meets nine times a year to discuss monetary policy and make possible changes.
An interest rate hike generally increases the demand for AUD increasing its value
An interest rate cut generally decreases the demand for AUD decreasing its value.
News Source: http://www.rba.gov.au/Statistics/cashrate_target.html
Australian Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
The GDP measures the final value of all goods and services produced within Australia’s borders during a specific period of time. GDP includes: private consumption, private investment, government expenditure and exports less imports.
During periods of constant growth inflation might become a problem for Australia’s economy.
With a good number, the AUD tends to gain value
With a bad number, the AUD tends to lose value.
News Source: http://www.abs.gov.au/ausstats/abs%40.nsf/mf/5206.0
Employment Change for Australia
This figure is the change of employment over a specified period of time. Usually traders and investors track employment data as a measure of the overall economy.
With a good number the AUD tends to appreciate
With a bad number the AUD tends to depreciate.
News Source: http://www.abs.gov.au/ausstats/abs%40.nsf/mf/6202.0
Consumer Price Index (CPI) of Australia
The CPI is the key element of inflation measurement. Basically inflation is the change in the purchasing power of one currency. Extreme inflation levels are no good for any economy, usually Central Banks tend to target values in-between.
A good CPI number tends to appreciate the AUD
A bad CPI number tends to depreciate the AUD
News Source: http://www.abs.gov.au/ausstats/abs@.nsf/mf/6401.0
Trade Balance of Australia
The Trade Balance of Australia measures the difference between exports and imports of Australia and their foreign trading partners. When this number is on the negative side, it means that imports are greater than exports, conversely when this figure is in the positive side, it means that exports are greater than exports.
With a good number the AUD tends to gain value against other currencies.
With a bad number the AUD tends to lose value against other currencies.
News Source: http://www.abs.gov.au/ausstats/abs%40.nsf/mf/5368.0
Switzerland – CHF
Switzerland Quick Economic Facts
Switzerland is the 19th largest economic power of the world with a GDP valued at over 380 USD billion. But on a per-capita basis, Switzerland is the 5th wealthiest country in the world.
The service industry, specially the banking, insurance and investment industries are very well developed and employ more than 60% of its population. These industries represent around 70% of the total GDP.
The Swiss National Bank (SNB) is responsible for the monetary policy in Switzerland. As other Central Banks, all decisions taken by the SNB are voted.
One difference between the SNB and other central banks is that monetary policy changes can be done at anytime. The SNB inflation target is below 3%.
Another difference is that the SNB doesn’t set an official interest rate target but a range target (i.e. 2.5%-3.00%) for their 3-month LIBOR rate.
The USDCHF has a very strong negative correlation (close to -1.0) with the EURUSD. So they both act as a mirror, when the EURUSD goes up, the USDCHF goes down and vice versa.
Switzerland is considered a safe-heaven.
Important Economic Indicators for the CHF
Interest Rate Announcement
As we already mentioned, the SNB doesn’t have a target rate but a target range for their 3-month LIBOR rate. The SNB mainly changes its target range to have some influence over inflationary pressure.
When the interest rate range is increased, the CHF tends to gain value.
When the interest rate range is decreased, the CHF tends to lose value.
News Source: http://www.snb.ch/e/geldpolitik/geldpol.html
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of Switzerland
Swiss GDP refers to all final goods and services produced within the national borders. The GDP growth in any economy is used to measure the overall health of the economy.
As a result of a good number the CHF might gain some value.
As a result of a bad number the CHF might lose some value.
It’s important to mention that if growth rates are high and consistent it might create inflationary pressure that can lead the SNB to increase the interest rate range. If GDP growth rates are low in the other hand, the SNB might respond lowering their target range.
News Source: http://www.bfs.admin.ch/bfs/portal/en/index/themen/systemes_d_indicateurs/economic_and_financial/data.html
Trade Balance
The Swiss trade balance measures exports less imports. When the country’s exports are larger than its imports the trade balance has a positive value. The first trading partner for Switzerland is the Eurozone followed by United States.
As a result of a good number, the CHF tends to gain value.
As a result of a bad number, the CHF tends to lose value.
News Source: http://www.snb.ch/e/publikationen/monatsheft/aktuelle_publikation/html/matrix_lists/e/statmon_I3.html
CPI
The CPI is the key element of inflation. Basically when the inflation rate grows the purchasing power of the CHF decreases and vice versa.
The SNB inflation target is below 3%
As a result of a good number the CHF tends to appreciate against other currencies.
As a result of a bad number the CHF tends to depreciate against other currencies.
News Source: http://www.bfs.admin.ch/bfs/portal/en/index/themen/systemes_d_indicateurs/economic_and_financial/data.html
Monetary Policy Assessment
Members of the SNB share their views of the current and future economic conditions.
Traders and investors tend to focus on key elements such as possible increases or decreases in the interest range target, inflation or growth.
News Source: http://www.snb.ch/e/publikationen/publi.html